What is RFID Labels?
1.Description
- RFID (Radio frequency identification): is a collection of smart labels that includes near-field communication (NFC) tags, ultra-high frequency (UHF) tags and more .
- If you are considering implementing an RFID solution, it is important that you understand the differences between each type of RFID.
- Choose a partner with experience in advising on the right card type for your business application.
2. So what is an RFID Labels?
- RFID technology relies on radio waves to send and receive information between the label and reader.
- At the simplest level, the RFID reader will send a signal to the RFID label and the label will send back a signal carrying the information.
Unique information is provided as a GS1 Electronic Product Code™ (EPC) - can be programmed into individual RFID tags that are then attached to products, boxes, pallets.
- Or even high-value devices depending on the application.
- RFID technology can be understood as barcodes, similar to barcodes.
- Tags RFID are often used to quickly trace product-level information.
- However, becauseRFID tags use radio wave technology, they do not require a direct line of sight to read.
- Meaning that an entire pallet or load of products can be read as fast as 700 products per second.
This gives RFID tags a clear advantage when it comes to driving supply chain tracking and optimization (known as smart label tracking). - In addition to distribution and supply chain benefits, many brands are taking advantage of RFID tags to engage customers in the experience.
- Allow consumers to scan labels to access educational programs or product-specific pages.
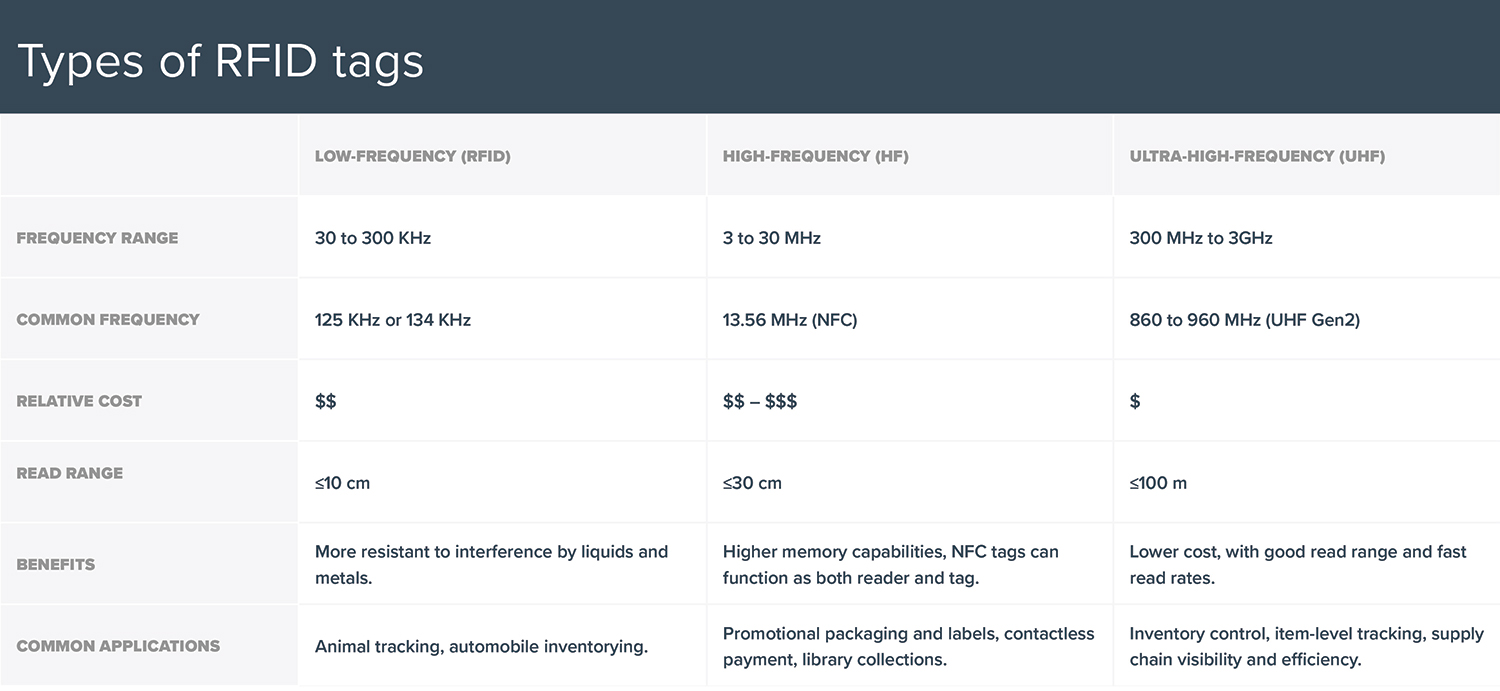
3. Types of RFID Labels
- In terms of frequency range, RFID labels have 4 different types:
- NFC (near field communication): near field communication card
- LF (low frequency): low frequency
- HF (high frequency): high frequency
- UHF (ultra-high frequency): super high frequency
4. Application, there are 3 types of RFID labels
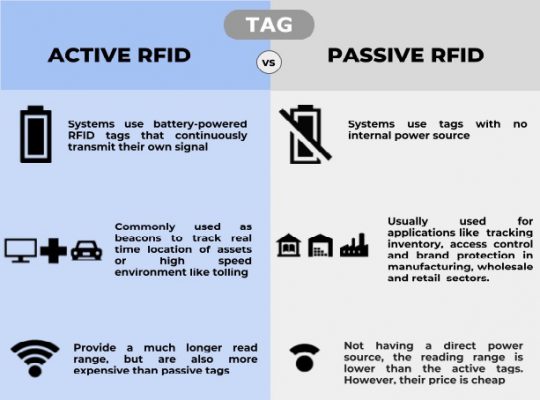
- Active:
- powered – has a battery and transmits signals periodically, useful in location tracking applications
- The battery in the active tag can increase the signal strength, the tag has a longer reading range, up to 100 meters.
- With the most expensive cost, this type of card is often used to track very high value assets:
- Construction equipment, automobiles or healthcare applications
- Passive:
- no power – the tag only works when it receives a radio signal from the reader
- Energy from the reader signal is used to turn on the tag.
- Transmits a signal that carries information back to the reader.
- Often used in tracking goods and pallets at low cost.
- Semi-passive:
- battery support – tag has a battery but does not transmit signals periodically like active RFID tags,
- Instead, the battery is only used to turn the card on when a signal is received
- This allows all the energy from the reader’s signal to be transmitted back.
5. Criteria for selecting a suitable RFID Tag:
- RFID tag frequency matches your needs.
- The size of the RFID label is suitable for the product to be affixed.
- Type of device to be pasted (Metal, non-metal).
- Single use or reuse.
- Adhesive strength for RFID Labels
- Product cost and investment level.
My name is Le Nam Viet, currently FOUNDER & CEO of Nam Viet IT Company, I graduated from Ho Chi Minh Polytechnic University. I have more than 3 years of experience providing RFID chip technology solutions, RFID scanners, barcode labels and barcode readers. It’s a pleasure to share my knowledge with readers.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt