The RFID Reader is an essential component in any RFID system. So, what exactly is an RFID Reader? How many types of RFID Readers are there? What are the criteria for choosing an RFID Reader? The following useful information from IT Nam Viet will help you better understand the role of RFID Readers.
What is an RFID Reader?
An RFID Reader (also known as a Radio Frequency Identification Reader) is a device used to identify objects and collect information from RFID tags, which are used to track individual items. Radio waves are used to transmit data from the RFID tag to the RFID Reader.

In simpler terms, an RFID Reader is a device used to read and collect data from RFID tags or transponders. This device uses radio waves to communicate with and gather information from RFID tags.
An RFID Reader can connect to a host computer system or via a network, transmitting and receiving data in various ways. However, experts believe that network-based connections allow the reader to operate more flexibly compared to direct computer connections.
How Does an RFID Reader Work?
An RFID reader consists of three main components: an antenna, a transceiver, and a decoder.
- The antenna emits radio waves and receives signals back from the RFID tag.
- The transceiver, implemented via a microchip, controls communication between the reader and the tag.
- The decoder interprets the data collected from the tag and sends it to the host system for further processing.
When an RFID tag enters the antenna’s range, it emits radio waves that are captured by the antenna. The transceiver then converts these radio waves into a readable data format. This information is then transmitted to the computer system, where it is stored and processed.
The distance at which the RFID reader can communicate with the tag depends on several factors, such as the frequency used and the reader’s output power. Active RFID tags, which have their own power source, can communicate over long distances, while passive RFID tags, which do not require batteries, typically have a shorter communication range.
Classification of RFID Readers
RFID readers can be classified based on various criteria. The most common way to classify RFID readers is based on their mobility.

Classification of RFID Readers by Mobility
Includes:
Fixed RFID Reader
Fixed RFID readers are typically 2-port, 4-port, or 8-port readers with high performance. The number of antennas depends on the coverage area required by the RFID system. Fixed RFID readers work with antennas, which provide the crucial link between the reader and the tag, facilitating the transmission of data back and forth. Antennas are an essential component of any fixed RFID system.
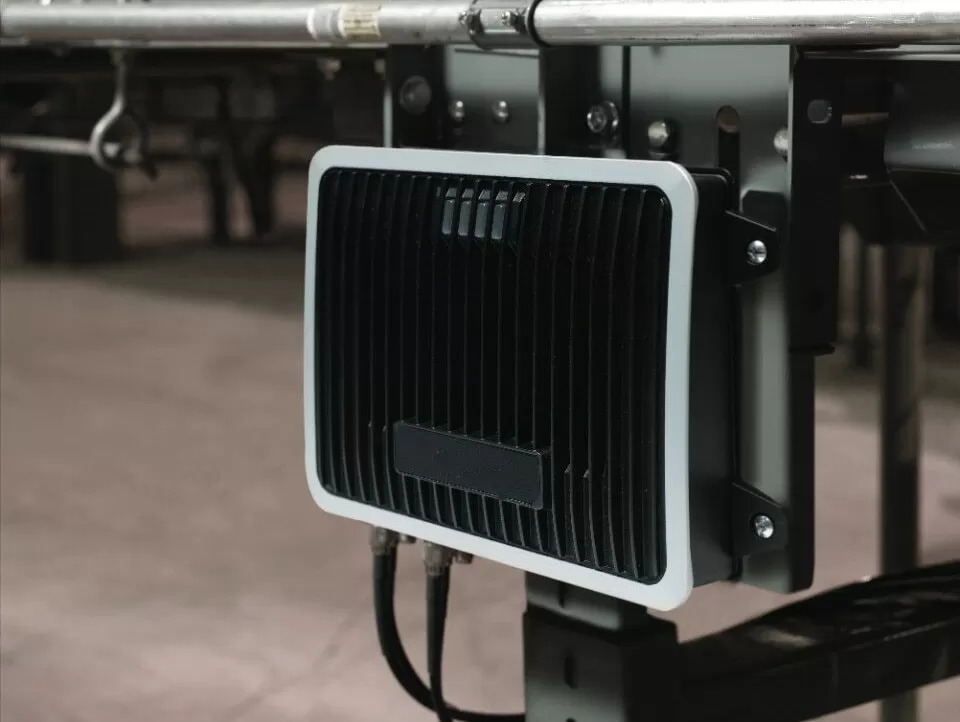

Integrated Readers are also fixed readers, but they combine both the RFID reader and antenna into a single complete device. Integrated readers typically offer medium performance, making them suitable for applications with a lower volume of RFID tags and smaller coverage areas.
Mobile RFID Reader
Mobile readers are handheld devices that can communicate with a host or smart device while reading RFID tags. Because handheld RFID readers are lightweight and battery-powered, they can be carried and used anywhere at any time.

Handheld radio frequency readers can also communicate with a host or smart device while reading RFID tags. Since handheld radio frequency readers are lightweight and battery-powered, they can be carried anywhere at any time. Compared to fixed readers, handheld ones don’t require installation and can read RFID tags simply by powering on the device. Additionally, they offer lower initial investment costs, more diverse application scenarios, and a wider range of data collection functions.
One of the most common mobile RFID reading devices is the smartphone, which also has an integrated antenna. These readers do not have antenna ports but come with many other features, powerful processing boards, and built-in operating systems that can run various programs and software while maintaining full functionality.
Moreover, there is a second type of mobile reader: Handheld RFID Readers. These small readers connect to smart devices via Bluetooth or auxiliary ports and can also be controlled using a smartphone.
Classification of RFID Readers Based on Other Characteristics
Currently, RFID readers can be classified based on various characteristics such as connection options, features, processing capabilities, antenna ports, etc. Some common types of RFID readers include:
- By frequency range: RFID readers for 902–928 MHz (US), 865–868 MHz (EU), etc.
- By connection options: WiFi readers, Bluetooth readers, LAN, serial ports, USB, auxiliary ports, etc.
- By available utilities: HDMI, GPS, USB, camera, GPIO, 1D/2D barcode, mobility capabilities.
- By processing capabilities: RFID readers with external or integrated processing.
- Power source: Power adapter, PoE, battery, vehicle-mounted, USB.
- By antenna ports: No external port, 1 port, 2 ports, 4 ports, 8 ports, or 16 ports.
Classification of RFID Readers Based on RFID Tags
Includes:
- Passive Reader Active Tag (PRAT): A passive reader that can receive radio signals from active tags (battery-powered tags that only transmit data). The operating range of a PRAT system can be adjusted between 1–2,000 feet (0–600 meters), allowing flexibility for applications such as asset protection or monitoring.
- Active Reader Passive Tag (ARPT): An active reader that can transmit query signals and also receive authentication responses from passive tags.
- Active Reader Active Tag (ARAT): Uses active tags with query signals sent from active readers.
For more details on RFID tags, readers can refer to the article: Common Types of RFID Cards and Their Applications
RFID Reader Connectivity
RFID readers are connected to computer systems or servers and transmit data in various ways, including:
Bluetooth Connection
Bluetooth is a protocol that allows RFID readers to connect to a host system wirelessly, without the need for cables. Most Bluetooth options are integrated into handheld devices like smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices.

WiFi Connection
Connecting RFID readers through a WiFi network is considered an effective wireless solution, allowing the reader to connect with printers and other smart devices. WiFi and LAN ports are often the only options if the application requires a network connection.
LAN (Local Area Network)
By connecting the RFID reader via a LAN, the reader can interact with all internal programs and devices within the company. In cases where the RFID reader cannot connect to the application via WiFi due to external factors, the LAN connection can serve as an alternative to ensure stable operation.
Serial Port
The serial port uses an RS232 or USB cable to connect directly to the host system. Connecting via a serial port optimizes simple applications with one RFID reader and a computer system, eliminating the need for internet connectivity for the reader.
Auxiliary Port
Some handheld devices can also connect to phones or tablets via auxiliary ports such as an audio jack or Bluetooth connection. The auxiliary port allows the RFID reader to connect to a phone in situations where Bluetooth is already in use by another device.
RFID Reader Pricing
The price of RFID readers is not fixed and depends on various factors such as:
- Type of RFID reader: Fixed or mobile/handheld.
- Frequency range: Low frequency, high frequency, or ultra-high frequency.
- Reading range: Short-range or long-range.
- Additional features.
In general, the price of RFID readers in the market can range from over $50 to several thousand dollars. At IT Nam Viet, with over 10 years of experience in distributing a wide variety of RFID readers, we are confident in providing our customers with high-quality, genuine products at the best prices on the market.

To receive the most accurate quote for RFID readers, please contact us via Hotline (+84) 962.888.179. The expert team at IT Nam Viet is ready to serve customers 24/7.
Criteria for Choosing an RFID Reader
Choosing the right RFID reader is crucial to ensuring the efficient operation of the entire RFID system. Here are the key criteria to consider when selecting an RFID reader:
- Consider the reading range of the radio frequency reader, whether it’s low frequency, high frequency, or ultra-high frequency.
- Assess the environmental conditions where the RFID reader will be used.
- Identify the type of surface for tag attachment, whether it’s plastic, metal, wood, etc.
- Evaluate the convenience of operation, which will help you decide between a fixed or handheld reader.
- Consider the number of tags that need to be read simultaneously and the speed at which the tags move through the reading area.
You may also require customizations to ensure the reader is compatible with your application. In addition to these factors, it is important not to overlook the importance of choosing a reliable distributor when purchasing an RFID reader. A trusted RFID reader distributor will give businesses peace of mind by ensuring strong sales policies, technical support, warranty, and after-sales services.
Expert Distributor of a Wide Range of Genuine RFID Readers at Competitive Prices
IT Nam Viet is proud to be one of the leading providers of trusted RFID solutions in Vietnam. With over 10 years of establishment and development, we specialize in offering RFID readers, RFID tags, antennas, barcode devices, barcode printers, and more, meeting the diverse needs of our customers.
All products distributed by IT Nam Viet are guaranteed to be genuine with clear origins. We have a team of highly experienced and skilled technicians who offer dedicated and thorough support to customers with the highest level of responsibility.
You can assess our credibility through various platforms, whether offline or online. IT Nam Viet provides 24/7 customer support, so if you need RFID or barcode services, don’t hesitate to contact us via Hotline (+84) 962.888.179.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt