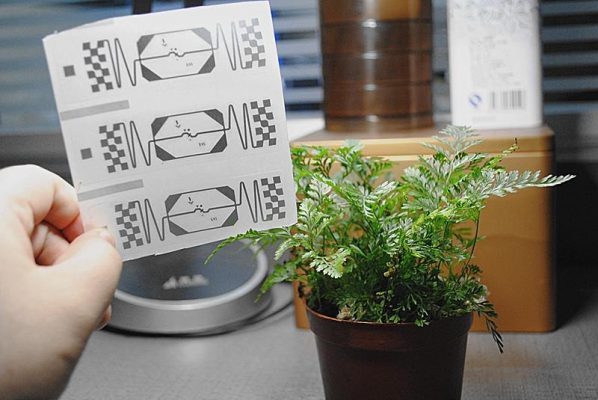
1. Definition of RFID Label
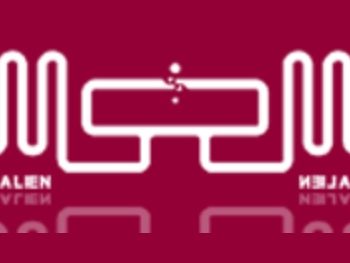
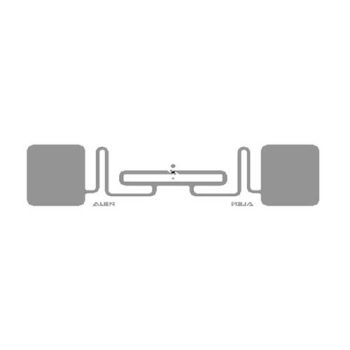
- RFID labels consist of 3 main components:
- Inlay (antenna): This device allows the RFID Chip to be attached and receives radio waves when transmitted to it.
- RFID Chip: The main device that receives radio waves from the reader through the RFID Antenna.
- Label: The material covering the Inlay where contents such as QR codes, product names, etc., can be printed.
- RFID Chip (Radio Frequency Identification):
- Is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects.
- An RFID system includes a small transmitter, a receiver, and a radio transmitter.
- When activated by an electromagnetic pulse to query data from a nearby RFID reader, the RFID tag responds with digital data, typically a formatted value unique to that tag, to the RFID reader.
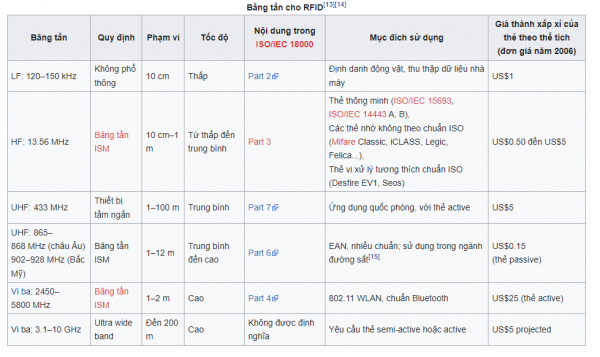
2. There are two types of RFID tags
- Passive tags:
- These tags are powered by radio waves transmitted from an RFID reader for data querying.
- The effective operating range of this type is from a few centimeters to several meters (M).
- Active tags:
- These tags are powered by batteries.
- They can be read from a considerable distance by an RFID reader.
- They can reach up to hundreds of meters.
- RFID Chip Brands:
- Alien RFID Chip
- NXP RFID Chip
- Monza RFID Chip
- And many other RFID label brands. However, these two brands are widely chosen by consumers.
3. Differences with Barcode:
- RFID labels do not need to be within the reading range of an RFID reader.
- They can be attached or embedded on objects that need to be tracked.
- Simultaneously monitor multiple objects with RFID tags.
4. Applications of RFID Labels in Reality
- RFID tags are widely used in industry:
- During automobile production, an RFID tag attached to a car being assembled can be used to track the entire manufacturing process on the production line.
- RFID tags attached to pharmaceuticals support tracking them in warehouses.
- Embedding RFID chips in livestock and pets supports animal identification.
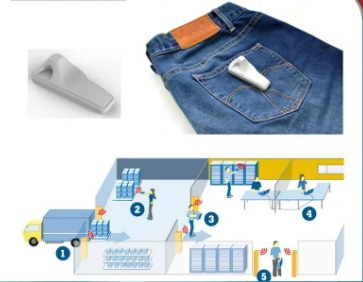
- RFID tags can also be used in the payment process at stores.
- And prevent theft of goods in stores.
5. Other Management
- Because RFID tags can be attached to physical devices such as assets, clothing, currency, or implanted in humans or animals, concerns about unauthorized access to information related to the owner of objects attached to these RFID tags have raised concerns about privacy rights.
- These concerns have led to the development of technical standards for RFID technology related to privacy and security.
- ISO/IEC 18000 and ISO/IEC 29167 use encryption methods on chips to prevent tracking, while authenticating tags and readers, and over-the-air privacy.
- ISO/IEC 20248 specifies an electronic signature with data structure for providing data, verifying sources, and reading methods of RFID and barcodes.
- This regulation is implemented by ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 31 (ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 31 Automatic Identification and Data Capture Techniques).
- A subdivision of ISO, and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Joint Technical Committee (JTC).


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt