Enhancing management efficiency, optimizing reader experience, minimizing unnecessary errors, and saving time and manpower effectively… these are the outstanding benefits that RFID technology brings to the management and operation of modern libraries. The following article will help customers understand more about RFID technology in the library sector, so don’t miss it!

Limitations in Traditional Library Management
The world is transitioning to integrate into the flow of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and naturally, Vietnam cannot be an exception to this trend. In this context, library systems need to make significant changes and apply technology in the management and operation of libraries.

Accordingly, the limitations in the traditional library management and operation include:
- The operation process is time-consuming: Library managers have to spend hours, even days, inventorying books and handling borrowing/returning procedures, while readers also spend a lot of time waiting and dealing with complicated procedures.
- There will inevitably be errors in library management: Naturally, this is unavoidable. Manual record-keeping will lead to discrepancies and omissions in managing thousands of books on various topics.
- The reader experience is still limited: With traditional operation methods, borrowing/returning books is quite time-consuming, and readers face difficulties in finding the books they want. This may cause readers to “turn away” and seek other reading sources from online channels.
- High operating costs: A traditionally operated library requires a large workforce to ensure all related tasks are fully carried out, such as book inventory, book arrangement, and handling administrative issues. This increases the operating costs of the entire system.
Thus, optimizing operating costs has become a challenge for some libraries today. The application of RFID technology in libraries helps address this issue by automating processes, reducing reliance on manpower, and significantly lowering operating costs.
Comprehensive Breakthrough RFID Solution for Libraries
The RFID library system applies RFID technology, combined with computer technology, programmable controller technology, network communication technology, and RFID tags to manage the library. The RFID library system not only provides readers with optimal borrowing and returning experiences but also enhances the library management method effectively, saving time and labor costs. This is considered a groundbreaking solution in the management and operation of modern library systems.

Efficiently Managing Thousands of Books
With the application of RFID technology, each book is equipped with a compact RFID tag containing information such as the book code, title, storage location, etc. Imagine each person has their own ID card; with RFID technology, each book also has its own “identity card.”
RFID has the capability of contactless operation, remote reading, fast reading, and reading multiple tags simultaneously, enabling quick, accurate, and efficient inventory management. Therefore, the application of RFID technology in libraries allows managers to easily inventory the entire collection of books without expending too much time and effort.
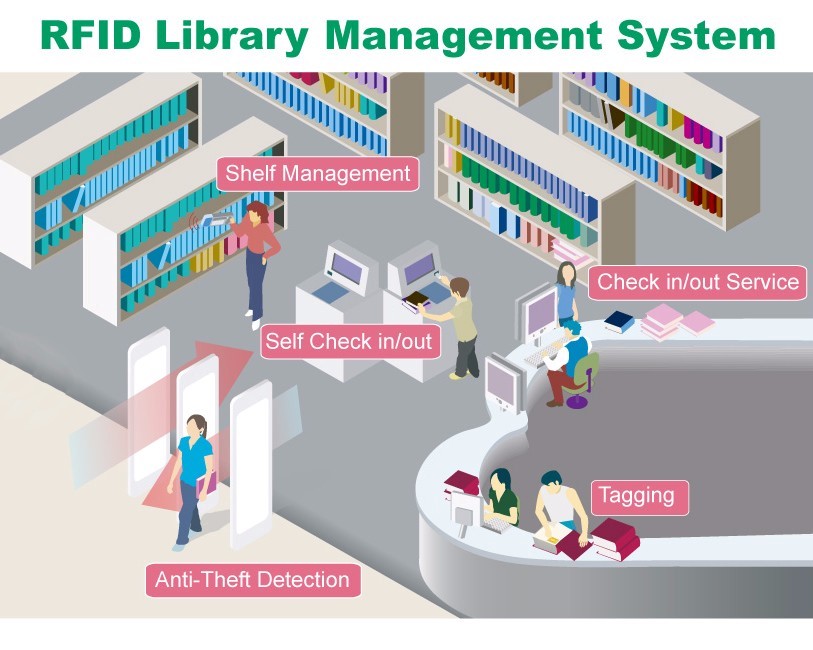
Furthermore, when an activated RFID tag is detected passing through, the security gate will trigger an anti-theft alarm. The tag’s anti-theft function is only deactivated when someone registers to borrow the book at the librarian’s desk or through the library’s self-checkout station. This helps prevent the loss of books and protects the library’s assets.
Additionally, the data collected from the RFID system is considered a ‘treasure trove’ that helps libraries better understand the preferences and needs of the majority of readers. This allows the library to plan book purchases and organize the collection more effectively, optimizing the library’s book inventory to ensure that readers’ needs are met in the best and most complete way, thus attracting and retaining readers more efficiently.
Enhancing the Optimal Experience for Readers
Especially with the automation of libraries through RFID technology, the borrowing/returning process becomes many times simpler, optimizing readers’ time effectively. Moreover, when they want to borrow or return books, readers no longer need to wait in line, as with just one scan, they can borrow or return multiple books at once—easily, quickly, and minimizing human errors.
Optimizing Library Services, Saving Operating Costs
With the library’s automation system through RFID technology, libraries can reduce staffing, restructure business processes, and significantly cut labor costs. This not only helps improve service quality but also meets readers’ demand for a digital, smart, convenient, and modern library. Furthermore, the self-service feature not only simplifies book borrowing and returning but also contributes to creating a friendly library environment for readers. This is a fundamental platform in the strategy of building libraries into centers for community reading and learning.
RFID in libraries not only helps optimize management processes but also significantly enhances the reading experience for readers. The use of RFID technology in libraries has become an inevitable development trend, leading to major changes in the library management and operation model.
Components of RFID Technology in the Library Sector
Accordingly, the RFID system in libraries consists of five main components, including:
Security Gate
When an activated RFID tag is detected passing through, the security gate will trigger an anti-theft alarm. The tag’s anti-theft function is only deactivated when someone registers to borrow the book at the librarian’s desk or through the library’s self-checkout station.
Librarian Station
Each RFID chip attached to a book is identified based on radio frequency signals. The librarian desk in the library is equipped with an RFID scanner and specialized software. With just one scan, readers can easily and quickly borrow or return books, optimizing their time effectively.
Self-Service Borrowing/Returning Station
In the library, self-service borrowing and returning stations are strategically placed to ensure reader satisfaction. Each station is equipped with a touchscreen that allows users to interact with the software to borrow or return books automatically without the need for any intermediaries. With this smart feature, readers will feel comfortable and satisfied whenever they visit the library, especially during peak hours.
RFID Reader
This is an essential component of any RFID-based management system, and library management and operations are no exception. You need to choose an RFID reader with high sensitivity, fast reading capabilities, stable operation, and especially good anti-interference features. Of course, balancing cost and functionality is a mandatory requirement to consider when investing in an RFID reader.
RFID Tag
The RFID tag is attached directly to each book and is designed in a square or rectangular shape. Beneath each RFID tag is a chip with the ability to emit radio waves, assisting with identification.
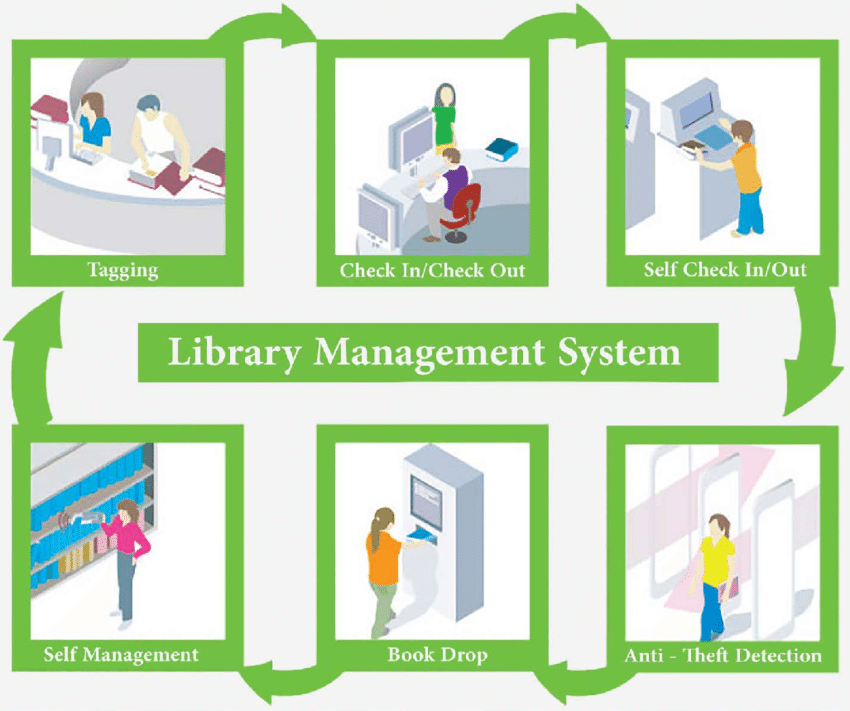
Operating Principle of RFID Technology in Modern Library Management
Accordingly, the operating principle of the RFID library system is as follows:
After being added to the library, books are tagged with an RFID tag and then programmed. The relevant information about each book is entered into the management system. At this point, the books are ready for borrowing.
Readers can borrow and return books in two ways:
- Borrowing and returning books through the librarian station: Here, the librarian will check the book’s code using an RFID reader and confirm the borrowing process. At this point, the chip in the RFID tag will be deactivated. Once deactivated, the book can be taken through the security gate without triggering an alarm.
- Borrowing at the self-service station: Here, the reader can borrow or return books on their own by following the instructions on the touchscreen. The tasks are performed similarly to borrowing/returning at the librarian station. Once the book is “checked out,” there will be no issue when passing through the security gate.
Finally, after the book is returned, either at the librarian station or the self-service station, the RFID tag is reactivated for the next borrowing/returning cycle.
Additionally, readers can return books through the 24-hour automatic book return system. This device is integrated with an automatic document sorting system.
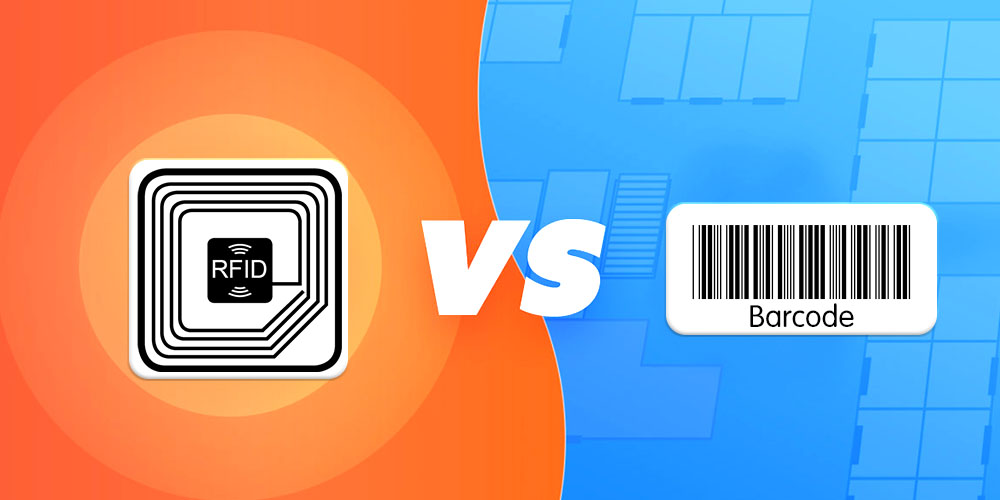
Comparison Between RFID and Barcode Technology in Libraries
To give you a clearer understanding of the superior advantages of RFID technology in libraries compared to barcode technology, please refer to the comparison table below:
| Criteria | RFID | Barcode |
|---|---|---|
| Operating method | Uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags. | Uses an optical reader to scan barcodes printed on surfaces. |
| Reading speed | Fast, can read multiple tags simultaneously within a certain range. | Slower, can only read one barcode at a time. |
| Reading range | Long, no direct contact needed, can read from several meters to tens of meters away. | Short, requires direct contact, usually readable within a few centimeters. |
| Data storage capacity | Large, can store a lot of information on RFID tags. | Small, only stores limited information on barcodes. |
| Durability | High, RFID tags are resistant to water, dust, and impact. | Low, typically single-use. |
| Security | High | Low |
| Cost | Higher compared to barcodes. | Lower compared to RFID. |

Currently, according to statistics, 2% of libraries in the United States have installed RFID technology, and 8% of libraries worldwide have adopted RFID technology. In Asia, RFID library systems have been applied in countries such as Thailand, Singapore, China, and Taiwan.
In Vietnam, until before 2015, not many libraries had successfully invested in and operated RFID systems. Notable examples include the libraries of well-known universities such as the Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam National University Hanoi, Nha Trang University, University of Transport and Communications, and Foreign Trade University.
However, nowadays, with more affordable RFID costs, tens of thousands of libraries worldwide are implementing RFID technology in the library sector. Vietnam is no exception, with a wave of libraries building plans to implement RFID.
IT Nam Viet – Specializing in High-Quality, Reliable RFID Solutions for Libraries
IT Nam Viet Trading – Service Co., Ltd. has become one of the few companies specializing in comprehensive technology solutions such as RFID chips (including custom RFID tags with specific sizes, antennas, and chips), RFID scanners, barcode tags, barcode scanners, label printers/ink, handheld Bluetooth printers, etc. With a professional, experienced team and advanced technology, we are committed to providing customers with complete satisfaction.
Don’t hesitate to contact the experts at IT Nam Viet. We will consult and provide you with suitable solutions and assist you in selecting professional products tailored to your needs.
IT NAM VIET TRADING – SERVICE CO., LTD
- Company address: 177/22 National Highway 1K, Linh Xuan Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Showroom and working address: VPGD 27/13/9C, Street No. 27, Hiep Binh Chanh Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City
- Phone: (+84) 962.888.179
- Email: Info@chiprfid.vn
My name is Le Nam Viet, currently FOUNDER & CEO of Nam Viet IT Company, I graduated from Ho Chi Minh Polytechnic University. I have more than 3 years of experience providing RFID chip technology solutions, RFID scanners, barcode labels and barcode readers. It’s a pleasure to share my knowledge with readers.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt













