RFID technology has been and is gradually being used in Vietnam in most fields. However, in reality, many users still do not clearly understand what is RFID? What does an RFID system consist of? How do they work?… The following article will help you grasp the basic knowledge about RFID solutions as well as their applications in life, follow it now and don’t miss it!

What is RFID?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. It’s a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system comprises a tiny transponder, a receiver, and a radio transmitter. When activated by an electromagnetic pulse from a nearby RFID reader to query data, the RFID tag responds with digital data, typically a unique identifier, back to the reader. This returned value can be used to track and manage goods, assets, control access, and much more.
Components of an RFID System
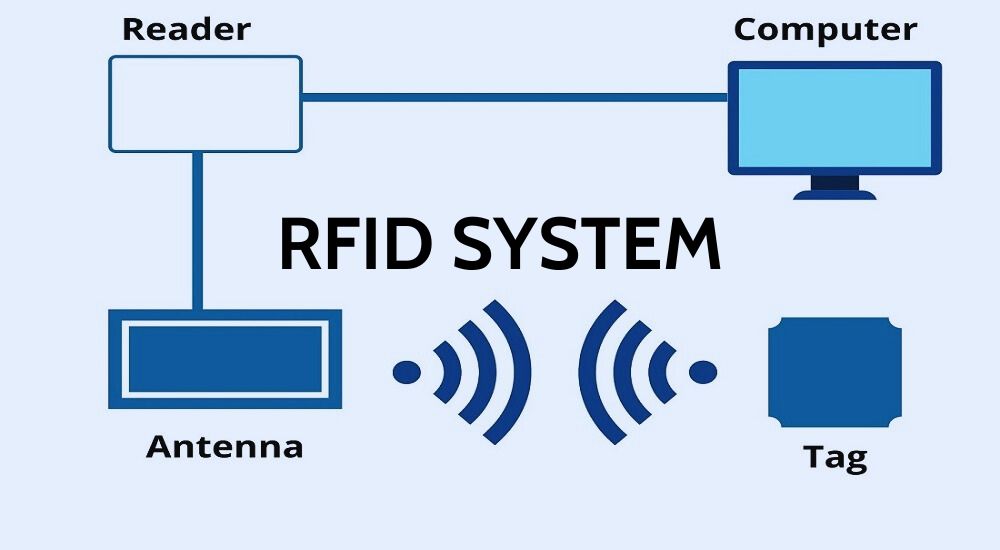
An RFID system consists of four main components:
RFID Tags: These are tags with a chip and antenna. There are two main types:
- Passive tags: Powered by radio waves emitted from the RFID reader, these tags have a shorter read range (from a few centimeters to a few meters).
- Active tags: These have their own power source (a battery) and can be read from much greater distances (up to hundreds of meters).
- You can learn more about the different types of RFID tags in our article: “Common Types of RFID Cards and Their Applications“.
RFID Reader: This device reads information from the tags. Readers can be fixed or mobile depending on the application and need.
Antenna: This is the link between the tag and the reader. The RFID reader emits radio waves to activate the tag and communicate with it.
Computer Software: This system collects and processes data from the RFID reader, enabling monitoring, statistics, and control within the RFID system.
Explore our wide range of RFID labels for various applications HERE:
How RFID Systems Work
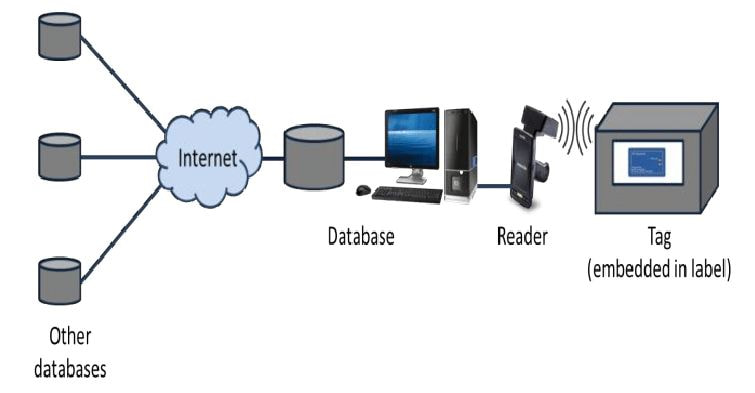
An RFID system uses tags attached to objects for identification. A two-way radio transceiver, known as an interrogator (or RFID reader), sends a signal to the RFID tag and reads the data it returns.
In simpler terms, the RFID reader emits electromagnetic waves at a specific frequency. RFID tags within the reader’s range absorb energy from these waves and transmit their unique identification code back to the reader. This allows the RFID reader to identify any tags within its operational zone.
RFID technology is now widely used across various sectors, including library management, warehouse management, and supply chain management.
For instance, in 2015, major universities in Vietnam, such as Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam National University Hanoi, Foreign Trade University, and University of Transport and Communications, implemented RFID technology to automate their library management systems.
Key Features of RFID Solutions
Here are three key features of RFID systems that set them apart:
No Line of Sight Required: Unlike barcodes, RFID doesn’t rely on light. It uses radio waves to communicate, so there’s no need for a direct line of sight between the tag and reader.
Contactless Data Transfer: RFID tags can transmit information wirelessly over short distances without any physical contact.
Readability in Challenging Environments: RFID can read tags through various materials, including concrete, snow, fog, ice, paint, and wood. This is a significant advantage over barcodes, which require a clear line of sight and struggle in harsh environments.
My name is Le Nam Viet, currently FOUNDER & CEO of Nam Viet IT Company, I graduated from Ho Chi Minh Polytechnic University. I have more than 3 years of experience providing RFID chip technology solutions, RFID scanners, barcode labels and barcode readers. It’s a pleasure to share my knowledge with readers.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt