RFID tag recording is an important step in implementing a radio wave management system. If scanning RFID tags helps collect data, RFID tag recording is the step of “identifying” the asset, turning the “inanimate” chip into a unique code representing the product. So what is RFID tag recording? How important is RFID tag encoding? What should be noted when recording RFID tags?… The following article by IT Nam Viet will help you answer the above questions in detail.
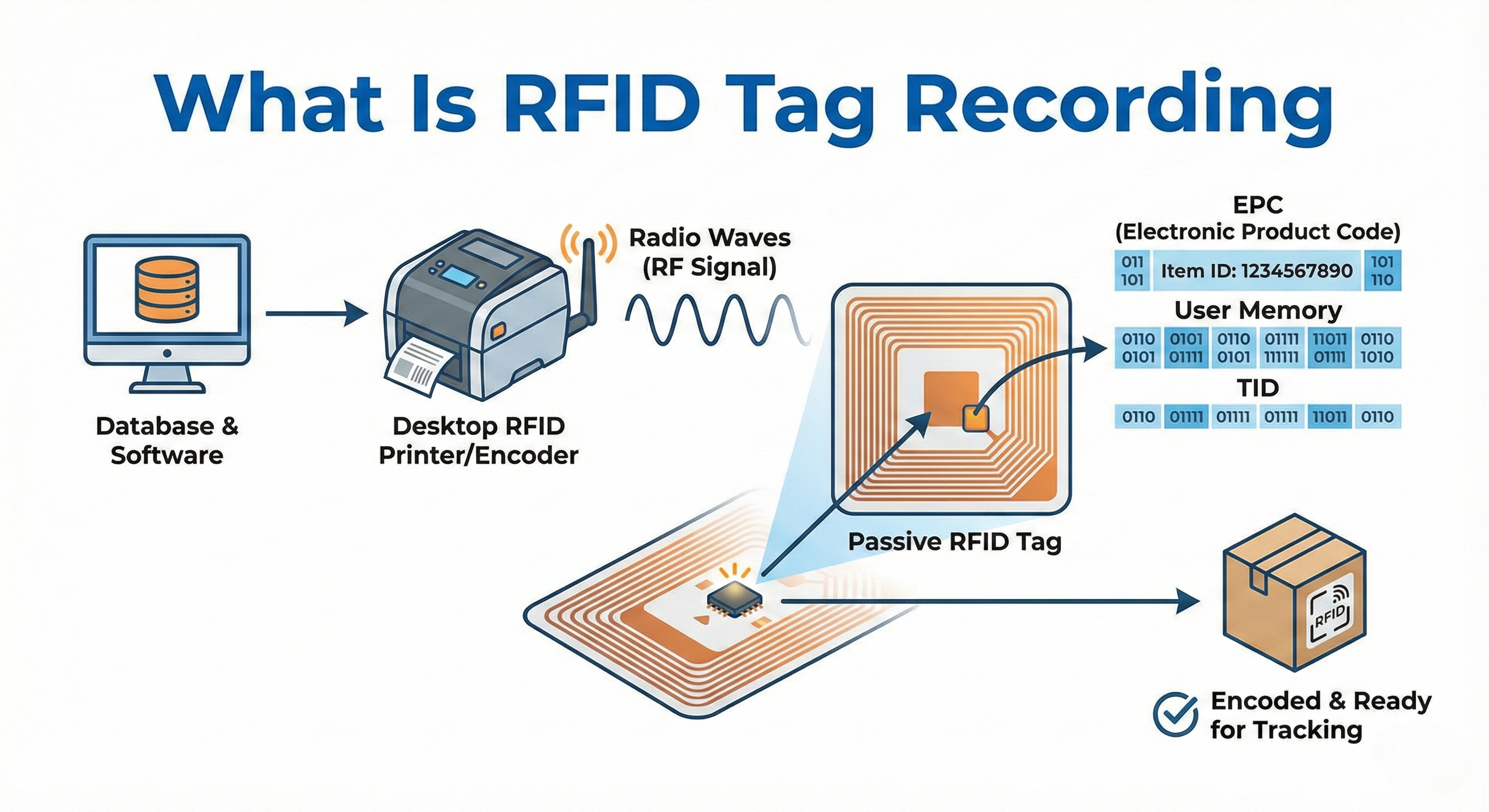
What is RFID Tag Recording?
What is RFID tag writing? RFID tag writing, also known as RFID tag encoding, is the process of writing specific information into the memory of an RFID chip. When newly manufactured, RFID tags (usually UHF RFID tags) contain only a unique ID code from the chip manufacturer (called TID) and the memory containing the product code (EPC) is usually left blank or contains a default random value.
In simpler terms, RFID tags have four memory areas: reserve memory, EPC memory, TID memory, and user memory. RFID tag writing usually refers to writing data to EPC memory or user memory. Writing data to RFID tags will ensure that each RFID tag has a unique identifier in the enterprise’s management system or ensure that the RFID tag’s identifier is synchronized with the enterprise’s EPC code on the GS1 system.
The Importance of RFID Tag Encoding
In fact, many new users still wonder why they don’t just use the default code of the card but have to encode the card? Encoding RFID cards will help synchronize data, standardize the supply chain,… For example, for retail corporations such as Walmart or Decathlon, encoding according to GS1 standards is required for goods to be accepted into the warehouse.
In addition, RFID card encryption will help lock data, prevent unauthorized access, enhance security and prevent counterfeiting or copying of RFID cards. On the other hand, card encryption is also applied to protect personal information stored on the card, protecting privacy absolutely.
In addition, RFID tagging also helps data to be organized more neatly in EPC memory, helping the reader to process many times faster than messy data.
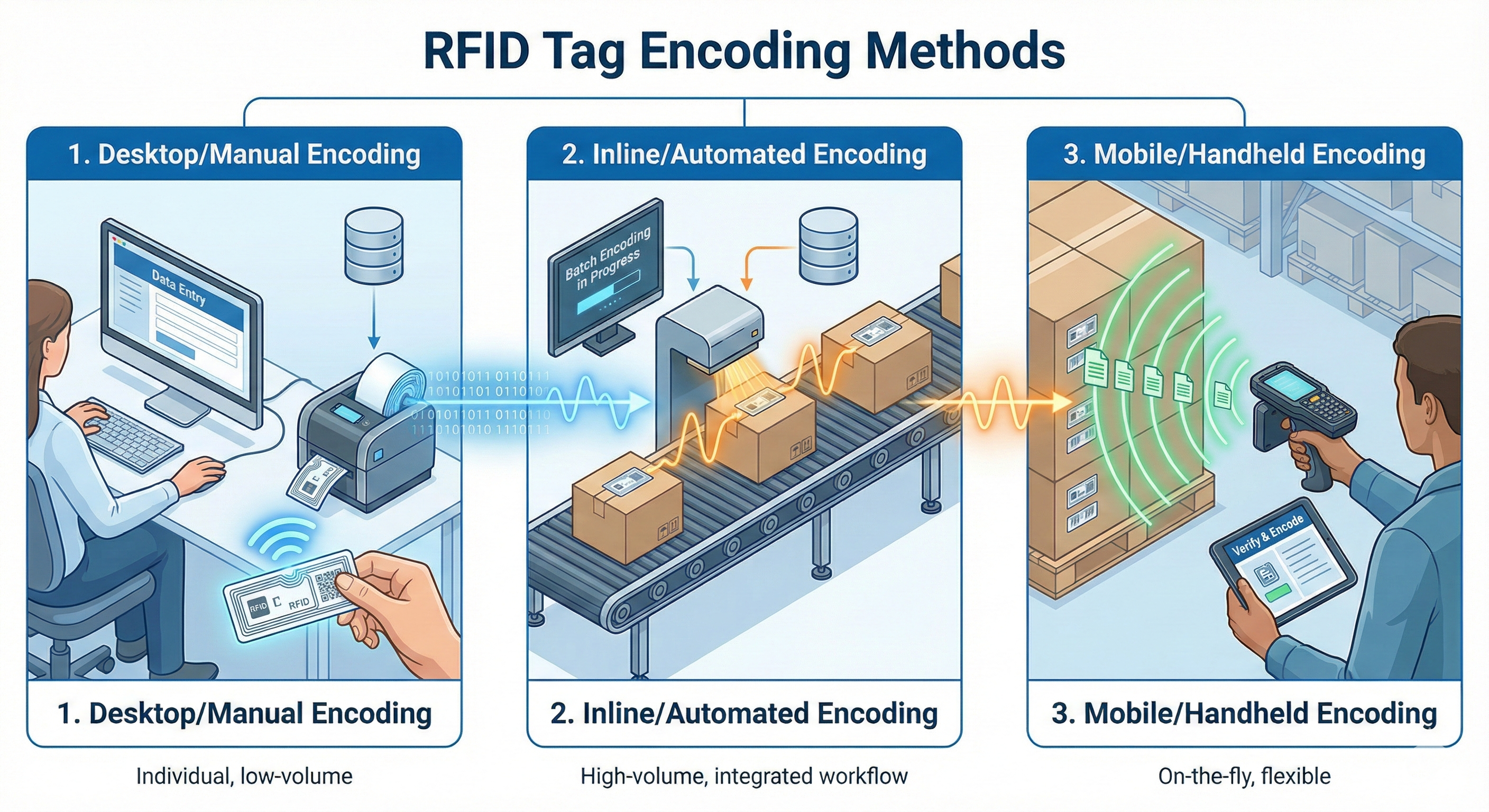
RFID Tag Encoding Methods
Accordingly, some popular RFID card encoding methods include:
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): This is a strong encryption standard widely used to protect sensitive data. The advantages of this method are strong security, difficult to attack, fast encryption speed, and is the optimal choice for RFID applications in Logistics, finance, anti-counterfeiting RFID, etc.
DES (Data Encryption Standard): This is an older encryption standard but is still used in some applications. The advantages of this method are fast processing speed, easy to deploy, low hardware resources, but short keys, no longer safe from current “attacks”.
3DES (Triple DES): This is a stronger version of DES, using three rounds of encryption to enhance security. The advantages of this encryption method are high security, compatibility with systems using previous DES, and is applied in some medium security RFID systems.
RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman): This is a public key encryption algorithm used for data protection and identity authentication. The advantage of this encryption method is that it is very strong in identity authentication and data protection, however, it is quite resource-consuming, less suitable for passive RFID, often applied in RFID bank cards,…
What Data Can Be Written to an RFID Tag?
Accordingly, there are 3 types of information that can be recorded on RFID tags, which are:
Random code
The company generates a random number as the primary ID of the card, then uses software to link this ID with relevant information in the database. Of course, this code ensures that there are no duplicates between cards. The random number is often written on RFID cards to prevent counterfeiting, secure the supply chain, etc.
Custom codes for specific listings
This is a more popular way to write on RFID cards, the code written on the card is synchronized with the ID list that the business has standardized in advance. The advantages of this RFID card writing method are transparent management, fast retrieval, easy multi-channel integration, applied in RFID asset management, RFID retail management, automatic warehouse,…
Other data
In addition, you can record some other data on the RFID tag such as production date, expiry date, warranty information, product configuration, etc. This data is usually located in user memory and can be encrypted to increase security.
Write RFID Tag With Custom Code
As mentioned, the unique identifier of an RFID tag can be a random number or a custom number according to a specific list. Accordingly, some cases of recording RFID tags with custom numbers are as follows:
- Recording the identifier is the serial number or product code, often used in RFID running and sports systems, or inventory systems, etc.
- Recording the identifier according to the enterprise’s EPC code: Enterprises apply GS1 standards to ensure that the EPC code is suitable for the global supply chain. The EPC code includes the Header, Filter Value, GS1 company code, item code, partition number and serial number. The most popular GS1 identification scheme is SGTIN-96.
- Recording the identifier in ascending order: The system creates a series of EPC codes that increase with each recorded tag, so managers can easily observe and compare the codes in sequence.
How Much Data or Numbers Can Be Written on an RFID Tag?
Accordingly, the number of characters that can be written on an RFID tag will depend on the data format (character encoding) and the available memory capacity of the tag.
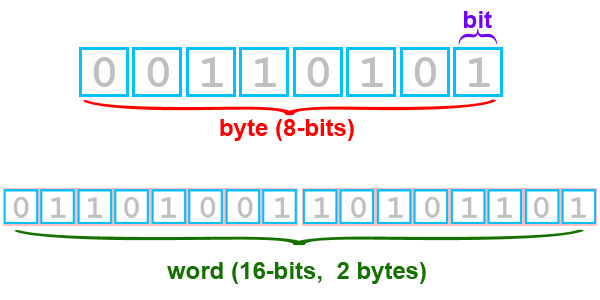
Bit data format
Bit is the basic unit of information and is what is transmitted and communicated between the RFID reader and the tag. Bits are encoded in a sequence of 4, using only the numbers 1 or 0. Using a sequence of bits to transmit data is called binary encoding.
Example of a 96-bit string:
01110010 01100110 01101001 01100100 01110011 01110100 01101111 01110010 01100101 00101110 01110110 01101110
As the EPC memory specification is 96 bits, it means that there will be a combination of 96 0s and 1s for communication between the tag and the RFID tag reader.
Hexadecimal format
Hexadecimal encoding is a method that uses only 16 types of characters, from A to F and from 0 to 9. Below is the representation of the above 96 bits of data in Hex form.
Hex: 7266696473746F72652E766E
Each hexadecimal character represents a string of 4 bits. So a 96-bit memory can hold 24 hexadecimal characters. Currently, most businesses will use hexadecimal encoding, meaning the RFID reader will receive and output data in HEX code. Businesses that want to convert from HEX to ASCII code will need to use custom RFID software.
ASCII format
ASCII, or American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a coding method that uses 128 specific characters, each represented by two 4-bit strings. ASCII can represent the entire alphabet (lowercase, uppercase, numbers 0–9, and some special characters).
Here is the representation of the above 96 bits of data in ASCII form:
ASCII: chiprfid.vn
Each ASCII character represents a string of 8 bits. Thus, a 96-bit memory can hold 12 ASCII characters. The tag’s EPC memory is always encoded in hexadecimal format, so if you want to convert to ASCII characters, you must use the ASCII – HEX conversion formula when encoding and reading back from the RFID tag.
Available memory capacity
To determine the available memory capacity of an RFID tag, businesses can refer to the RFID tag specification description. Businesses can use the table below to determine the maximum number of encoded characters corresponding to the tag’s EPC memory.
| RFID tag EPC memory | Maximum number of encoded characters |
| 32 bit | 8 hexadecimal characters |
| 64 bit | 16 hexadecimal characters |
| 96 bit | 24 hexadecimal characters |
| 128 bit | 32 hexadecimal characters |
| 256 bit | 64 hexadecimal characters |
Applications of RFID Tag Encoding
Nowadays, RFID tagging is widely used in many different applications, including:
- Access control to buildings, offices, restricted areas.
- Encoded RFID cards for payment of goods and services.
- RFID card encoding applications in supply chain goods tracking.
- Encoded RFID cards can be used to track patients and their medical records.
- Card encoding applications in RFID non-stop toll collection.
- RFID card recording applications in asset management, warehouse management,…
Notes When Encoding RFID Cards
When encoding RFID tags, it is important to note that:
- The type of encoding used should be appropriate to the level of security required for the data.
- RFID tag encoding can directly affect the overall system performance, so you must choose an RFID tag encoding method that ensures a balance between security and performance.
- The RFID tag encoding method should be chosen to be compatible with the RFID reader as well as the system components.
- In fact, you must understand that the cost of RFID tag encoding can vary depending on the application method, so depending on your budget, you should choose the appropriate tag encoding method.
RFID tagging is the step of converting digital data into physical signals attached to the product. Understanding and complying with international coding standards will help the RFID system operate smoothly and stably. If you need advice on coding solutions or RFID readers, RFID cards, RFID printers, etc., please contact IT Nam Viet via Hotline (+84) 962.888.179!
My name is Le Nam Viet, currently FOUNDER & CEO of Nam Viet IT Company, I graduated from Ho Chi Minh Polytechnic University. I have more than 3 years of experience providing RFID chip technology solutions, RFID scanners, barcode labels and barcode readers. It’s a pleasure to share my knowledge with readers.


 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt